![]()
Create a new logical location format
Copy a logical location format
Delete a logical location format
Add items to a logical location format
Add Attributes to logical location format
Remove items from a logical location format
Example logical location format
A logical location format is used to automatically divide your logical typicals in a project. Within a logical location format you can define a set of rules which determines the location of logical typicals in the logical location tree (project). A logical location format contains all your defined logical template types. Each template type in a location format contains ten 'Level names' and ten 'Level descriptions'. This means you can generate a maximum of ten levels in your project. The 'Level names' determines the names of the levels, the 'Level descriptions' the descriptions of the levels. You can export the list of logical location formats to Excel by clicking Export excel.
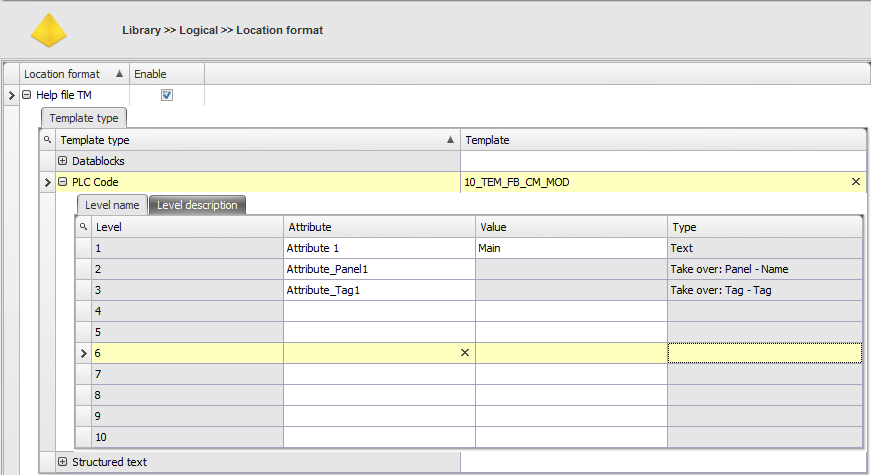
As you can see in the picture below, we have three template types.
See also:
Click .
Enter a unique name.
Instead of creating a new logical location format from scratch, an existing logical location format can also be copied.
Select the logical location format to copy.
Click .
Enter a new, unique name for the copy.
Optionally change the linked templates and attributes.
Select the logical location format to remove.
Click .
Click in the message dialog.
Notes:
1. A logical location format which is used in a project cannot be deleted.
(Templates and attributes)
Select the item to add to a template type (template) or level (attribute) from the library panel.
Drag the item to the desired template type/level.
Additionally, you can fill in a default value for an attribute on a level.
Each level in the location format can have 2 attribute, these attribute will be used when auto dividing a logical typical in project.
Base on the attribute value (Name), in project, a location (template) is found or created to place the typicals in.
The description will also be set based on the given attribute value.
If in the project no attribute is found, the default value will be used.
Not all attributes can be used within a location format.
Attribute that can not be used:
Take over: Electrical location
Take over: Logical location
Take over: Scada location
Take over: I/O
Take over: I/O Channel
Template types cannot be deleted from a location format. You need to delete a template type in the Template type window.
To delete a template from a template type, click on the small 'X' in the template cell.
To delete an attribute from a level, click on the small 'X' in the attribute cell.
In the example below you can see we used three attributes on the first three levels. Because typicals in a logical module are linked to a logical template type, Typical Manager knows on which template the typical must be positioned and at which level the typical must be positioned.
See also: