![]()
You can add ‘Expressions’ to attributes. With an expression builder you can create your own expression for each attribute.
![]()
In the ‘Expression’ column, click on the three dots. A pop-up window appears. This is the ‘Expression builder’ or ‘Expression Editor’.
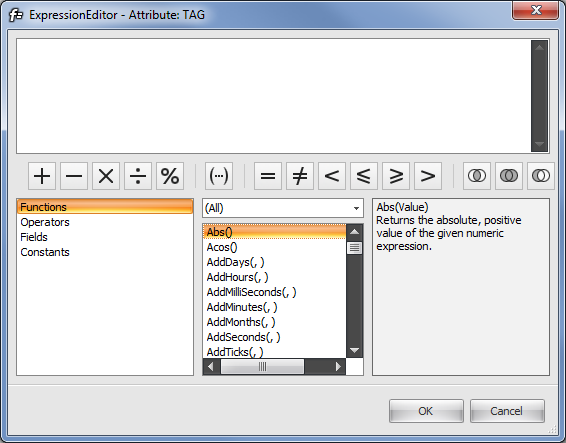
The expression builder has four sections. The top section is the editor, here you can create your expression. On the most left section, you see four categories. The center section shows functions, operators, fields or constants, dependent what you choose on the left section. The most right section shows information about what you select in the center section.
Choose ‘Functions’ on the left and scroll down in the center section till you see function “Substring('', , )”. With this function you can retrieve a substring from a string. With a double-click the function appears in the editor. Now we must enter a String, StartPosition and a Length: Substring('String', StartPosition, Length). For String we want the value of the attribute. Delete the two quotes in the function and select ‘Fields’ on the left screen. Double-click on ‘[ValueAsText]’ to use this field in your expression. Fill in 2 and 4 respectively at StartPosition and Length. Your expression will now look like this:
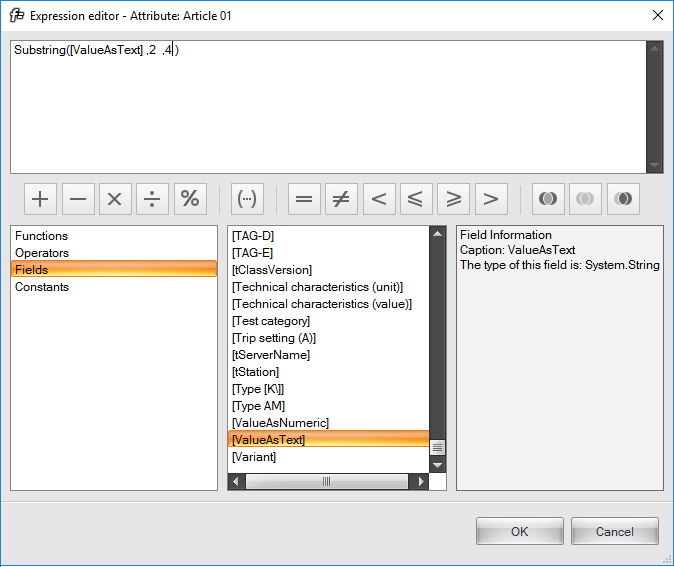
Click on OK and your expression is ready.
Notes:
1. If the expression is wrong or the expression can’t return a value, Typical Manager® will leave the attribute empty. For an example. If you use the expression Substring([ValueAsText], 2, 4), and the attribute value is ‘Test’, the expression can’t return a value because the attribute value has only 4 characters. Begin counting from 2 with length 4 isn’t possible.
2. The result of an expression is only graphical, it won’t be written to the database. The original value is the value from the database.
3. If you have an expression on a ‘Lookup list’ attribute, the result of the expression must be one of the values which are available in the lookup list. If you use a ‘Numeric’ lookup list, you also must take into account the ‘Unit’.
4. Attributes with an expressions contains a tooltip which shows the expression, the original value and the actual value. This tooltip is available in every window of Typical Manager®.
5. Expressions are case sensitive. So [ValueASTEXT will not work.
See also:
The attribute expression can use different kind of fields in expressions.
Field:
[ValueAsNumeric]
[ValueAsText]
[<AttributeName>]
With the use of the correct expression it is possible to get field values from other attribute inside a module, product, template, ect.
The field list will be filled with all attributes that can be used within that attribute expression.
By using the flowing expression "[Cable length (m)]" the value as text of the attribute "Cable length (m)" is retrieved.
If the expression uses a numeric attribute the 'value as numeric' used for calculation
If the expression uses a selection attribute the true/false value is used for if statements
with other attributes the 'value as text' is used.
when an attribute requires a different value from the attribute a value propertie is used.
Expression format: [{AttributeName}].[{RequiredValue}] or [{AttributeName}.{RequiredValue}] (e.g "[Cable length (m)].[ValueAsText]" )
This can also be used for [ValueAsNumeric]
This expression will only work if the attribute with the expression and the attribute that is used within the expression are both in the same 'owner'.
An 'owner' can be a:
Module (e.g. Electrical module or Logical module)
Template (e.g. Scada template or document template)
Product
Panel
Project
Note:
With expressions it is not possible to retrieve attribute values from attribute in other modules of products.
To do so, see: Attribute relations
When an attribute name is changed. Any Expression that uses that attribute will also be changed with the new attribute name.
See also:
It is possible to change expressions for attribute used on Modules, Templates ect. (See owners above)
When doing so the 'Expression editor' is shown, and in the field list only the attributes are visible that exist within the 'owner'.
Changing an expression will only be set in derived attributes which have the same expression.
So if expressions are changed inside modules / products (owners), then these expressions are not overridden when the attribute definition is changed and the attributes on module/ products (owners) have different expressions.
Note:
It is also possible to change expressions by copy and paste the cell or text.
Variable types:
Attribute variable types TM |
Variable type |
Example |
Text |
String |
‘This is a string’ This is not a string |
Numeric |
Int or double |
2 or 2,3 |
Choice |
Bool |
TRUE or FALSE |
Article |
String (Article number) |
MOE.PKZM0-4 |
Lookup list |
Text or Numeric |
Hello or 3 |
Examples:
Attribute type |
Value |
Expression |
Result |
Text |
CONTROL VALVE |
Substring([ValueAsText], 2, 4) |
NTRO |
Text |
|
Now() |
01-01-2013 00:00:00 |
Text |
|
Substring(‘Testing’, 0, 3) |
Tes |
Numeric |
10 |
ToInt([ValueAsText]) / 2 ([ValueAsNumeric] / 2) + 10 |
5 15 |
Numeric |
|
Now() |
01-01-2013 00:00:00 |
Choice |
True |
Iif([ValueAsText] == 1, TRUE, FALSE) |
False |
Article |
MOE.PKZM0-4 |
Substring([ValueAsText], 1, 3) |
OE. |
Lookup list |
Hello |
Iif([ValueAsText] == 'Yellow', 'Bye' , 'Sky') |
Sky |
Lookup list |
1 mm |
Iif([ValueAsText] == '1mm', '1 mm' , '5 mm') |
1 mm |
|
|
|
|
Text |
|
[Project.Name] |
Name of the project of the attribute |
Text |
|
[Panel.Name] |
Name of the panel of the attribute |
Text |
|
[Module.Name] |
Name of the module of the attribute |
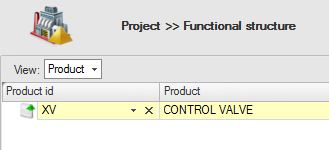
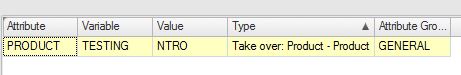
In this case we have a ‘Take over: Product –Product’ attribute. So, if you use this attribute in a Product, the [ValueAsText] will retrieve the Product name as a string (therefor we don’t need the quotes). So, if the name of the Product is ‘CONTROL VALVE’, this attribute will show ‘NTRO’. Startposition is 2 (begin counting from 0) and Length is 4, and as a result of that we get ‘NTRO’:
Beside the [ValueAsText] field, there are some other fields which can be used in attribute expressions. These fields work like the [ValueAsText] field. Instead of [ValueAsText] you can use the following fields:
Attribute type |
Remark |
Expression |
Result |
Text |
Only for Project attributes |
[Project].[Name] |
Name of the project |
Text |
Only for Panel attributes |
[Panel].[Name] |
Name of the panel |
Text |
Only for attributes in modules |
[Module].[Name] |
Name of the module |
Other examples:
[Project].[ProjectId]
[Project].[Principal]
[Project].[PrincipalId]
[Project].[EndUser]
[Panel].[Description] (Any '[Panel]' expression is only possible for panel attribute and attributes in an Electrical Module)
[Module].[Enabled]
[Module].[Selected]
[Module].[Group]
[Module].[SubGroup]
[Module].[Description]
[Module].[Function]
[Product].[Id]
Article attribute expressions:
An article attribute can work with special article expressions. These expressions makes it possible to get specific data from an article attribute. For the expressions to work, the article attribute need to have an article selected. The special expressions work like the [ValueAsText] field. Instead of [ValueAsText] you can type [Article].[******]. Where the ****** are shown, you can fill in a column name which you can find in the article settings in library.
Examples:
Expression |
Result |
| [Article].[Description1] | Gets the first description of the article |
| [Article].[Type_number] | Gets the type number of the article |
| [Article].[*Some other available column name* ] | Gets the data of the named column from the article |
Notes:
1. When a column name has spaces in between, you can fill these up with a "_" in the expression.
2. These special expressions are case sensitive. So [Project].[PROJECTID] will not work.
See also: